Engineering
- Basic principles of Engineering:
- Reproducibility (do the same thing more than once),
- Measurability (define what is same),
- Portability (as a result of the above),
- Standardization (formal or industrial),
- Documentation (what else is needed for reproducibility),
- Organization (no randomness).
- Apply these principles in Software Engineering.
Application
- Application is a computer program created for users.
- Application can be logically divided in followint parts:
- Presentation layer
- input, display results, user interface, logic of user interface
- Application layer
- data processing, calculations, business logic
- Data layer
- storage and retrieval of data, storage logic
- Presentation layer
Birth of application
- Includes:
- analysis of requirements
- architecture design
- choice of technologies
- programming
- testing
- Choice of technologies and architectural desing are usually caried out together
- Computer is really needed only for programming and testing
- Application also has to be deployed and maintained
- Includes end of life procedures
Step 1 - analysis of requirements
- Most important part of whole development process
- Depends on experience, size of team/company (yours and customer’s), budget, …
- Requires analys of customer’s environment
- Different approach for different types of customers
- Significant impact on the outcome
- Project cartoon
Step 1 - analysis of requirements
- General (non-functional)
- Web/desktop/console application
- Operating system and technologies
- What the appliction should do (functional)
- List of use-cases + scenarios
- Who will use the application
- User roles and other actors (time, other apps)
- How the user interface should work
- Graphical design / wireframes / no UI at all
- What kinds information will be stored (if any)
- Interfaces for other applications (if any)
Step 2 - architecture
- Structure and distribution of application’s services
- presentation layer
- presentation services (display UI elements)
- presentation logic (UI layout and function)
- application layer
- logic of application (application algorithms)
- logic of data storage (data algorithms)
- data layer
- data control (storage access control)
- presentation layer
- Generally a 3 layer architecture is most suitable
- Yet a 2 layer application is used sometimes
- Multiple variants
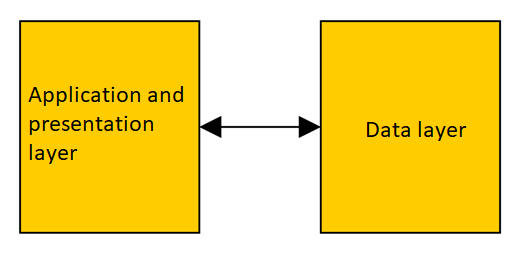
Two layer - option 1
- Client-server with remote data storage (file server)
- Heavy load on client
- Heavy load on transmission channel
- Small load on server
- Examples:
- SVN, DFS, NFS
Two layer - option 2
- Client-server with remote presentation
- Small load on client and transmission channel
- Heavy load on server
- It is impossible to distinguish from three-layer architecture from client’s perspective
- Many web applications
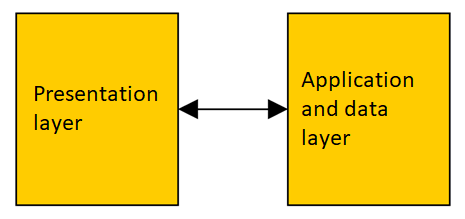
Two layer - option 3
- Client-server with separated logic
- Good load balance
- Diffucult to expand and/or port application logic
- Some very complex web applications
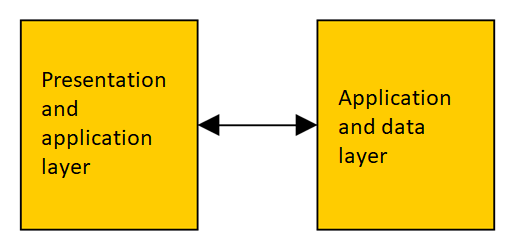
Two layer model
- Data are stored in format given by needs of application - diffuclt to transfer between applications
- Data store change requires all clients to reflect that change
- Reasons to use:
- quick first desing and implementation
- unavailable or non-developed universal solutions
- database servers
- application servers
- components
Three layer model
- Good load balance
- Small load on transmission channel
- Good expandability
- When using standardized interfaces
- Flexible architecture
- Example of many web applications
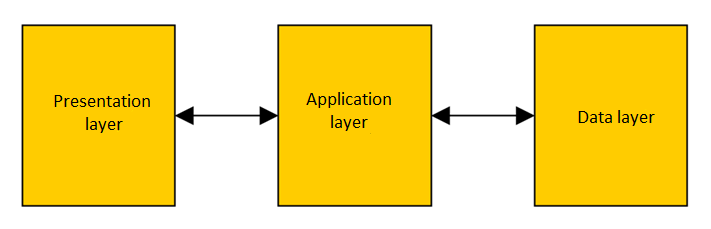
Three layer advantages
- Presentation and data layer are separated by application layer
- client presentation can be changed when using appropriate interfaces
- web app/mobile app with single backend
- data storage can be changed when using appropriate interfaces
- ORM
- change in presentation layer cannot influence data storage
- flexible, safe, reliable
- client presentation can be changed when using appropriate interfaces
- Interface is something between two things
- well documented communication protocol
Example
- Application rendered in web browser does not depend on a database server
- Is is not important where data was gathered
- We can change data store completely and presentation will remain same
- Application can be viewed in different browsers and data store is not aware of this
- Application layer is an interface between data store and presentation layer
Distributed systems support with three layer application
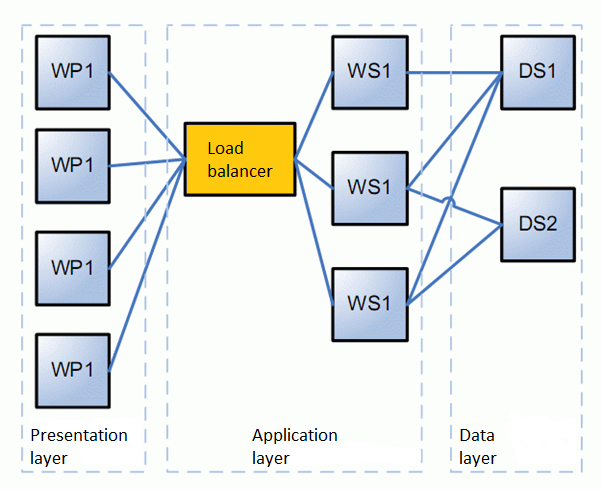
SOA, API
- An application with good API can be used from another applications
- Presentation layer can be bypassed and work directly with application from another app code
- A good interface uses well known standard format (SOAP, XML-RPC - XML, REST - JSON, XML) and is documented
- More such apps is used to create new application by combining existing abilities
- Cloud services
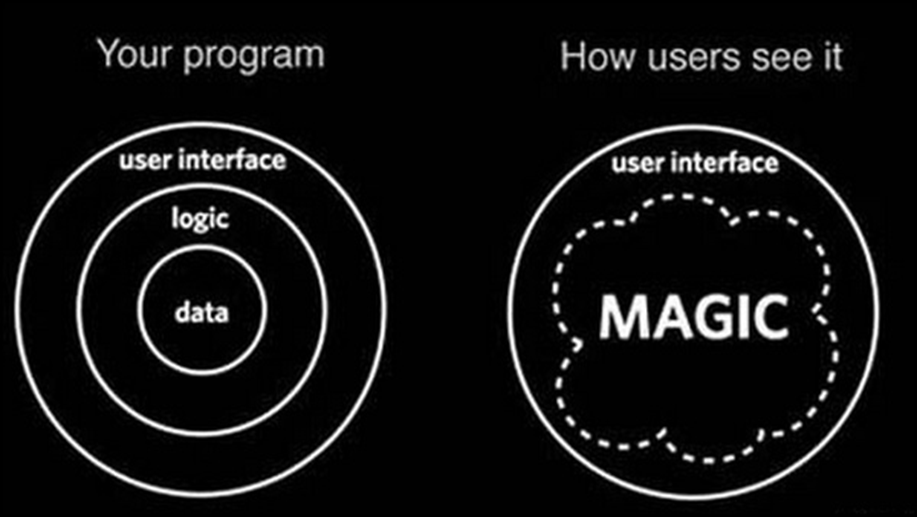
Step 3 - Technologies
- By requested application properties:
- network / local
- client-server / stand-alone
- compiled / interpreted
- native / runtime
- Database application
- Web application
- Language and development environment
- not just IDE
- Available libraries and their distribution system
Different approaches
|
↑ Increases
|
↓ Increases |
Web applications
- Web page only delivers content (read only)
- Web application interacts with user
- Advantages
- Rapid development (RAD)
- Portability
- Low operational maintenance costs
- A lot of prepared and well documented services (HTML, CSS, Web browser)
- Disadvantages
- A programmer cannot influence many things in presentation (given by browser)
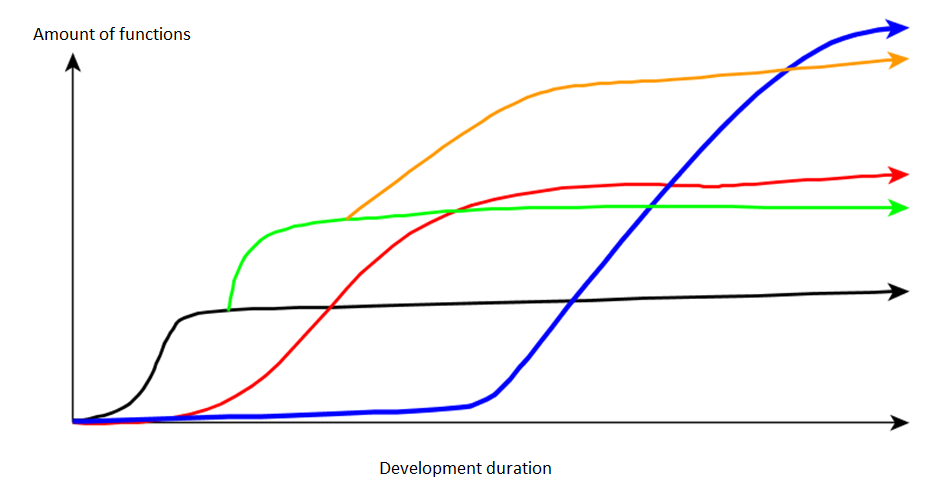
An impossible chart
Checkpoint
- Why a user should not communicate directly with data layer?
- Does every web application have to have an API?
- Which layer is best to solve a request that “searching for products should not be influenced by diacritics”?
- Is it better to have more or less application layers?
- Does web/network application have to have client-server architecture?
- Is is better to choose architecture or technologies first?
- What is important to choose a technology?